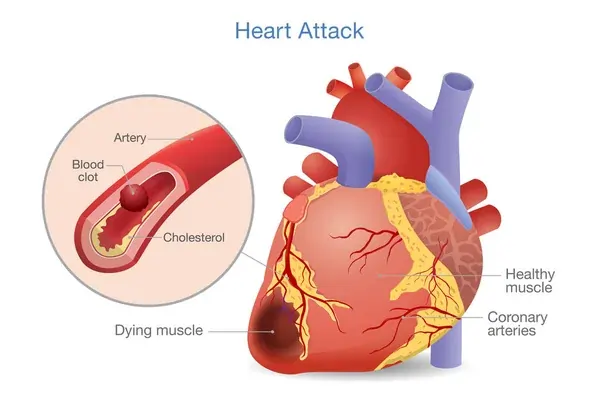
Heart attacks, or myocardial infarctions, are often associated with older adults, but increasing numbers of younger individuals are experiencing these life-threatening events. This worrying trend has brought to light several risk factors and underlying causes that can contribute to heart attacks in young people.
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics play an important role in heart health. Some people inherit conditions that make them more likely to develop heart disease at an early age. For example, familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder characterized by extremely high levels of LDL cholesterol, which causes premature heart disease. Similarly, conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) can increase the risk of heart attack in young people. Early screening and genetic testing can help identify people at risk and enable proactive management.
2. Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle factors are important in the development of heart disease, even in young individuals. Diet plays an important role; A diet rich in saturated fat, trans fat and cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, where arteries become clogged with plaque. Additionally, consuming excessive amounts of processed foods and sugary drinks can aggravate these conditions. Physical inactivity is another major contributor. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to obesity and related conditions such as high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, which are risk factors for heart attacks. Encouraging regular physical activity and a balanced diet can reduce these risks and improve overall heart health.
3. Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress and poor mental health are increasingly recognized as important factors in cardiovascular health. Young people experiencing high levels of stress, anxiety or depression may be more vulnerable to heart disease. Stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking or excessive drinking, which further increases the risk. Mental health issues can also affect physiological processes like blood pressure regulation and inflammation, which contribute to cardiovascular problems.
4. Smoking and Substance Abuse
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for heart disease, and its effects are particularly harmful when combined with other risk factors. Young people who smoke are more likely to develop atherosclerosis and have an increased risk of heart attack. Similarly, abuse of drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines can trigger heart attacks by causing severe vasoconstriction, high blood pressure, and arrhythmias.
5. Chronic Conditions
Many chronic conditions that are increasingly being diagnosed in younger populations can contribute to heart attacks. For example, diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, is becoming more prevalent in young adults and the risk of heart disease increases significantly. High blood pressure, often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle, is another important factor. It is essential to manage these conditions through lifestyle changes and medical treatment to reduce the risk of heart attack.
6. Undiagnosed Heart Conditions
Some heart conditions may not be diagnosed until they cause something serious. For example, conditions such as congenital heart defects or myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) may not be identified until a heart attack occurs. Regular checkups and paying attention to symptoms like unexplained chest pain or shortness of breath can help catch these issues early.
7. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Modern life presents a variety of environmental stressors and lifestyle choices that can contribute to heart disease. Excessive use of electronic devices, irregular sleep patterns and exposure to pollutants can affect heart health. Maintaining a healthy balance in lifestyle choices, ensuring adequate sleep, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins can support heart health.
Conclusion
Although heart attack at a young age may seem uncommon, it is a growing concern that highlights the need for awareness and prevention. By understanding the various causes, from genetic factors and unhealthy lifestyle choices to stress and chronic conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health. Regular medical checkups, a balanced lifestyle and attention to mental health are important to reduce the risk of heart attacks and ensure a healthy future.